ABSTRACT
A visualization display network is created such that images to be displayed at the visualization presentation center(s) are formatted for direct display on the viewing terminals without requiring significant additional processing at the visualization presentation center.
For example, the display terminals at the visualization presentation center may be configured to display signals received in a standard color format such as RGB, and the signals output from the visualization processing center and transported on a switched underlay optical network may be formed in the same color format. A visualization transfer service is provided to reserve resources on the switched underlay optical network and to coordinate visualization events between the visualization processing center, network, and visualization presentation center. Network resources may be scheduled in real-time on-demand or may be scheduled to be provided at a predetermined optionally under-constrained time.
Transporting visualization information on a switched underlay network
An Inventor: Dr. Tal Lavian
BACKGROUND
1. Field
-
This application relates to communication networks and, more particularly, to a method and apparatus for transporting visualization information on a switched underlay optical network.
2. Description of the Related Art
-
Data communication networks may include various computers, servers, nodes, routers, switches, hubs, proxies, and other devices coupled to and configured to pass data to one another. These devices will be referred to herein as “network elements,” and may provide a variety of network resources such as communication links and bandwidths. Conventionally, data has been communicated through the data communication networks by passing protocol data units (or cells, frames, or segments) between the network elements by utilizing one or more types of network resources. A particular protocol data unit may be handled by multiple network elements and cross multiple communication links as it travels between its source and its destination over the network.
- Conventional data networks are packet switched networks, in which data is transmitted in packet form which allows the packets to be commingled with other packets from other network subscribers. As the size of a data transfer increases in size or the sustained bandwidth required for the transmission increases, the ability to handle the data transfer on a packet network decreases. For example, a traditional packet switched network, such as a TCP/IP based communication network, will tend to become overloaded and incapable or inefficient at handling large data transfers or high bandwidth data transfers. Thus, it is desirable, at least in some instances, to obtain a dedicated path through the network to handle the transfer.
- One application that requires a very high sustained transmission rate is high resolution visualization. For example, visualization processing may be performed by a group of processors and then presented on one or more high resolution display monitors at a visualization presentation center. The computers performing the visualization processing in the visualization processing centers may process multiple terabytes of data to generate a series of high resolution images, which must then be transported to the visualization presentation center to be displayed. Where the resolution is required to be high, the amount of data required to generate the visualization presentation can become very large. For example, assume a 9 megapixel display monitor is driven at 30 frames per second, and each pixel requires 24 bits of information per frame. The bandwidth required to drive this display is 9,000,000 pixels times 24 bits/pixel, times 30 frames per second, or 6.48 gigabits per second. Where there are 8 monitors in the display, 15 monitors in the display, or more, as is becoming common in high resolution visualization presentation centers, the required data throughput from the visualization processing center to the visualization presentation center quickly increases to a sustained data transmission rate approaching or exceeding 100 Gbps.
- Because of these extremely high data rates, conventional packet networks are ineffective or incapable of transporting high resolution visualization information. Accordingly, processing facilities for very high resolution visualization have conventionally been provided in the vicinity of the display facility to avoid transporting the data long distances on a network. This limits the ability to have the display viewed by persons not present in the visualization presentation center and dramatically increases the cost associated with creating new visualization presentation centers.
SUMMARY OF THE DISCLOSURE
-
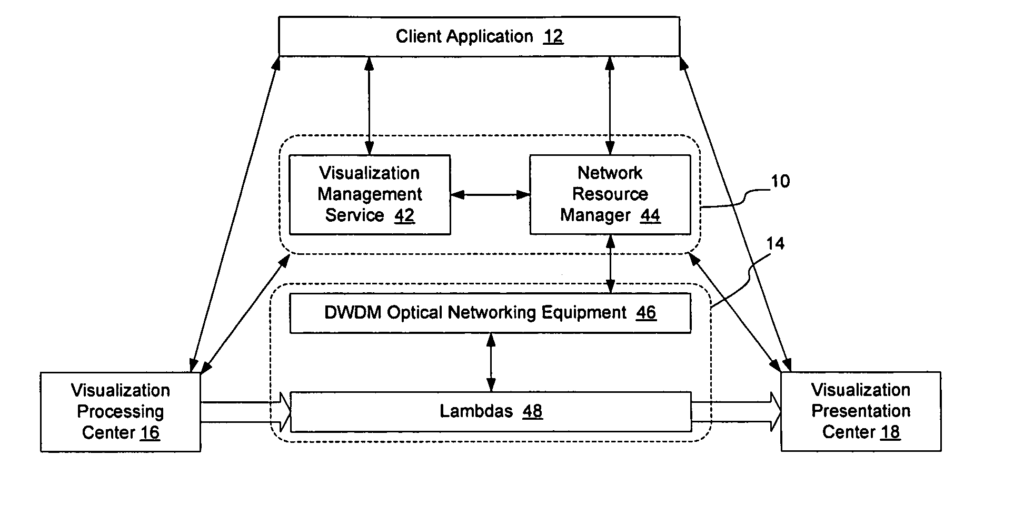
As described in greater detail herein, a method and apparatus for transporting visualization information on a switched underlay optical network enables network resources to be obtained for the transmission of visualization information such that high data rate visualization information may be generated at a visualization processing center and transported in real time or at a scheduled time to a remote visualization presentation center. According to an embodiment of the invention, network resources may be scheduled in real time on demand or may be scheduled to be provided at a predetermined optionally under constrained time. This allows optically switched scheduled resources to be provided on a switched underlay network, so that the network can transport visualization information for a visualization event from a visualization processing center to one or more visualization presentation centers.
- According to one embodiment of the invention, a visualization display network is created, such that images to be displayed at the visualization presentation center(s) are formatted for direct display on the viewing terminals without requiring significant additional processing at the visualization presentation center. For example, the display terminals at the visualization presentation center may be configured to display signals received in RGB format, and the signals output from the visualization processing center and transported on the switched underlay network may be formed in RGB, YUV or another color format, and may also be encoded according to a conventional television encoding standard such as one of the HDTV standards. In this manner, the processing requirements at the visualization presentation center, and hence the cost of the visualization presentation center, may be minimized. Optionally, according to one embodiment of the invention, the video monitors forming the visualization presentation center may be connected directly to the network to allow direct visualization from the transported images.