ABSTRACT
System to provide ratings and corresponding feedback for enhancing the genuineness in the ratings.
Embodiments of the invention provide means to the system’s users to provide ratings and corresponding feedback for enhancing the genuineness in the ratings.
The system includes a memory coupled to a processor. The memory consists of one or more instructions executable by the processor to enable the system’s users to rate each other based on at least one of sharing, exchanging, and selling one activity, service, or product. The system may provide a mechanism to encourage genuineness in ratings provided by the users. Furthermore, the instructions facilitate the rating receivers to provide feedbacks corresponding to the received ratings. The feedback includes accepting or objecting to a particular rating. Moreover, the memory includes instructions executable by the processor to enable the system to determine the genuineness of an objection raised by a rating receiver.
Rating system for determining – user in social network
An Inventor: Dr. Tal Lavian
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
Social networking applications – enhancing the reliability of ratings provided to users in a social network.
The invention relates to social networking applications, and more specifically, the invention relates to enhancing the reliability of ratings provided to users in a social network.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
In the current scenario of global inflation, resource management is increasingly required to cut the cost and overcome many other problems.
For example, the prevalent use of single-occupancy vehicles is a significant cause of several major economic, social and environmental problems. The problems include increasing costs due to energy resources for each car, higher parking-space issues, traffic congestion, increased air pollution, and the like. Further, an alternative to single-occupancy vehicles is multi-occupancy vehicles, where multiple individuals can share a single car.
For sharing a resource such as a vehicle, an individual needs to search for people willing to join for transferring a car for riding together to a particular location. This requires spending time searching for reliable people to share the ride. Further, in existing systems, a user can post a query for vehicle sharing. Corresponding to the post, other users of the system who are interested in sharing the vehicle for the ride (from now on may be referred to as “interested users”) can reply to that query regarding their interests in sharing the car. However, in these systems, the interested users may be completely unknown to the user who posts the question. Thus, the main problem in such systems is the lack of credibility in the interested people, which typically is the prerequisite for many users.
Further, in these systems, the user has to wait until any interested user responds corresponding to the user’s query. Furthermore, the user may need to contact the other interested users, either personally or telephonically, to discuss various parameters for sharing the vehicle. Such parameters may include but are not restricted to compensation/expense that may be shared between the users, timings, and various conditions corresponding to the sharing of vehicles for a ride. This wastes a significant amount of time on the user’s part.
Further, in addition to vehicle sharing, some other resources may not be shared, generally, with others, such as houses, machinery, etc. Further, such non-sharable resources may be expensive to possess. An individual may think of providing or receiving such a resource in exchange for any other aid or service. However, exchanging such expensive resources with any additional help or assistance offered by any other person requires a high level of credibility in the other person’s offer and vice versa. Further, suppose an individual decides to exchange a resource with a service offered by the other person. In that case, the individual may be required to keep an eye on the other person’s activities (corresponding to the service). This wastes a significant of time for the individual to track the service provided by the other person. For example, a user may think of reducing a cost by borrowing a piece of machinery from any other person (possessing the machinery) in exchange for providing some service to the other person, such as pets’ keeping in the absence of the other person. Here, the other person has to have trust in the individual to allow the individual to handle the pets in the absence of the other person. Thus, the credibility of any unknown users for exchanging the product/service remains always at stake.
In addition to resource sharing and exchanging, many individuals like to look for people for collective activities, such as recreational activities. An individual usually searches for like-minded people for any recreational activity, such as playing, riding, etc. For example, an individual may be willing to dine with someone or maybe ready to play chess with someone good at (or interested in) playing chess. For this, the individual may be required to spend a considerable amount of time searching for any person around who is like-minded and credible to go along with for any such collective activity. In such cases, the credibility of any unknown person is always a question for the individual.
Based on those mentioned above, there is a need for a system and a corresponding method to support resource sharing with credible users and without requiring much time consumption at a user’s end. Further, the system should provide support for collaborative or exchangeable activities with reasonable and suitable users based on a user’s interest. Furthermore, the system should support a user for sharing and/or exchanging services or products. Thus, the system is required for providing support to a user in sharing/exchanging resources/services and to overcome the shortcoming of the related arts.
SUMMARY
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system for enhancing the reliability of ratings provided to users in a social network.
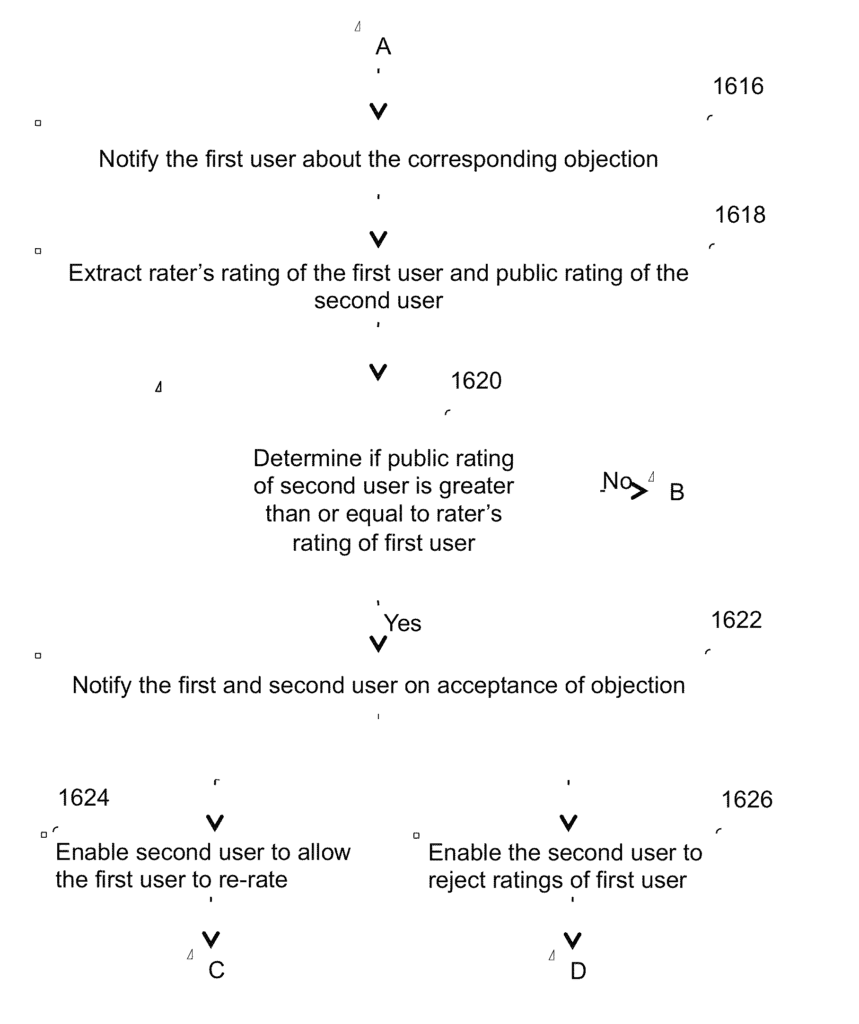
The system includes a processor and a memory coupled to the processor. The memory consists of a database and instructions executable by the processor. The database provides profile information (corresponding to each user) that may include information corresponding to one or more types of ratings received by each user based on sharing, exchanging, and selling at least one activity, service or product. Furthermore, the instructions enable the second user to object to the rating provided by the first user. Also, the objection raised by the second user may be accepted or rejected by analyzing the information corresponding to at least one of the one or more types of ratings corresponding to the first user and the second user. Additionally, at least one of the types of ratings corresponding to the users may be updated based on acceptance or rejection of the objection raised by the second user.
Further, embodiments of the present invention provide a system for enhancing the reliability of ratings provided to users in a social network. The system includes a processor and memory. The memory comprises a database and instructions executable by the processor. The database may contain profile information corresponding to each user that corresponds to one or more types of ratings received by each user based on at least one of sharing, exchanging, and selling at least one activity, service, or product with one or more other users. Further, the instructions analyze the rating provided by the first user concerning a pre-set value of rating to determine whether the rating is above, below, or equal to the pre-set value of rating. Furthermore, instructions may perform one or more tasks to enable at least one of the first user and the second user to perform one or more acts corresponding to the rating, the at least one of the first user and the second user is enabled to perform the one or more actions based on analysis of the rating. Additionally, the instructions executable by the processor may update the types of ratings corresponding to the users, based on the one or more acts performed by at least one of the first users and the second user.