ABSTRACT
Dynamic assignment of classes of traffic to a priority queue.
Bandwidth consumption by one or more types of packet traffic received in the packet forwarding device is monitored to determine whether the bandwidth consumption exceeds a threshold. If the bandwidth consumption exceeds the threshold, assigning at least one type of packet traffic of one or more types of packet traffic is changed from a queue with a priority to a line with a second priority.
Traffic classes to a priority queue in a packet forwarding device
An Inventor: Dr. Tal Lavian
Telecommunications, and more particularly, the dynamic assignment of traffic classes to queues having different priority levels.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
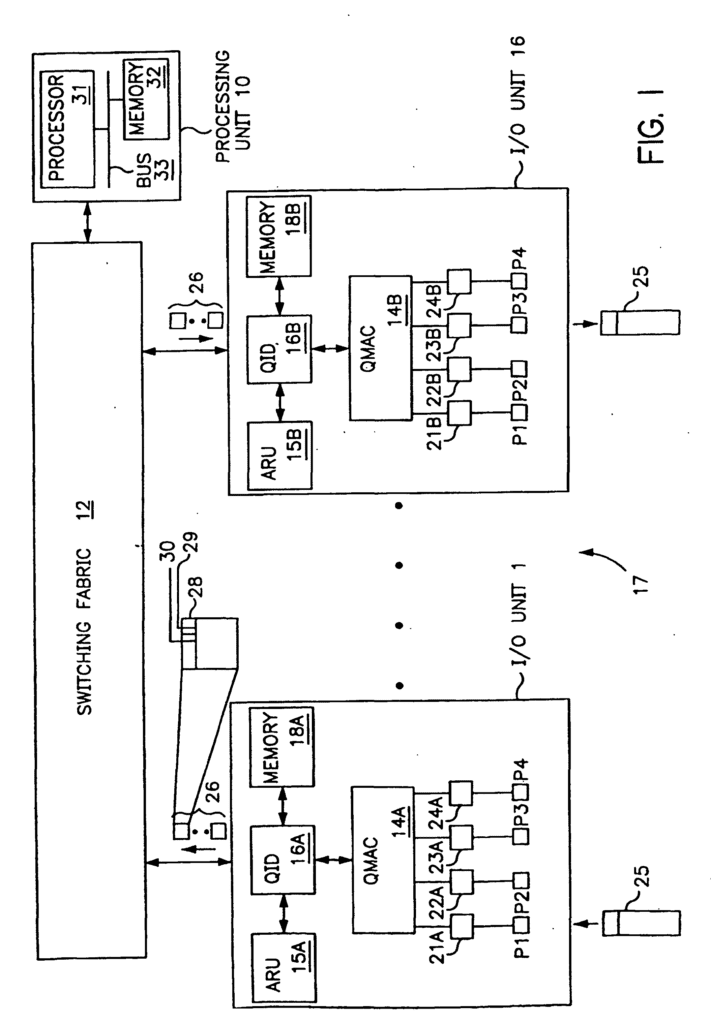
The flow of packets through packet-switched networks is controlled by switches and routers that forward boxes based on destination information included in the packages themselves.
A typical switch or router includes several input/output (I/O) modules connected to a switching fabric, such as a crossbar or shared memory switch. In some switches and routers, the switching material is operated at a higher frequency than the transmission frequency of the I/O modules. The switching fabric may deliver packets to an I/O module faster than the I/O module can output them to the network transmission medium. In these devices, packages are usually queued in the I/O module to await transmission.
One problem that may occur when packets are queued in the I/O module or elsewhere in a switch or router is that the queue delay per packet varies depending on the amount of traffic the controller handles. Variable queuing delays tend to degrade data streams produced by real-time sampling (e.g., audio and video) because the original time delays between successive packets in the stream convey the sampling interval and are therefore needed to reproduce the source information faithfully. Another problem resulting from queuing packets in a switch or router is that data from a relatively important source, such as a shared server, may be impeded by data from less important sources, resulting in bottlenecks.
One possible solution to this is described in International Application Number WO 99 00949. In this application, a method whereby queues are prioritized is disclosed, and the priority of a flow may be lowered. However, flows are packets forwarded within the subnet, requiring no header modification. Therefore, a method for prioritizing packets from/to sources/destinations outside the subnet is required.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A method and apparatus for the dynamic assignment of traffic classes to a priority queue per Claims 1 and 9, respectively, are disclosed. Bandwidth consumption by one or more types of packet traffic received in a packet forwarding device is monitored.
The queue assignment of at least one type of packet traffic is automatically changed from a queue with priority to a line with a second priority if the bandwidth consumption exceeds the threshold.
Other features and advantages of the invention will be apparent from the accompanying drawings and the detailed description below.